Serial Ata Cable Pinouts
Serial ATA is the next-generation internal storage interconnect, designed to replace parallel ATA technology. Serial ATA SATA, is a computer bus technology designed.
Serial ATA SATA, abbreviated from Serial AT Attachment 2 is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk.
Many serial communication systems were originally designed to transfer data over relatively large distances through some sort of data cable. The term serial most.
Pinout of Serial ATA SATA power connector and layout of 15 pin SATA power connector.
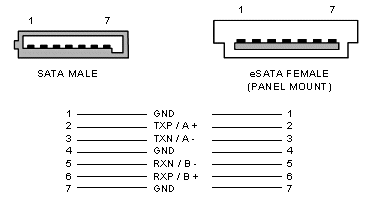
Serial ATA (SATA) pinout
EIDE / PATA Cable Pinouts. What shall we call these devices. In the beginning, or at least around 1986, was Western Digital s Integrated Drive Electronics IDE.


Serial ATA (SATA) power connector pinout

Handbook of hardware pinouts, cables schemes and connectors layouts.
Here is a list of pinouts associated with 9 pin D-SUB female connector : 9 to 15 pin VGA cable pinout; Ablerex Troy 600 UPS cable pinout; ADC Pairgain 310F and 320F.
Molex 67581-0000 used for cable connector and Molex 67582-0000 used for terminals connector. The SATA standard specifies a power connector sharply differing from those used by PATA drives and many other computer components. It is wafer-based, 15-pin shape. The seemingly large number of pins are used to supply three different voltages — 3.3 V, 5 V, and 12 V. Each voltage is supplied by three pins ganged together (and 5 pins for ground). This is because the small pins cannot supply sufficient current for some devices. One pin from each of the three voltages is also used for hotplugging. The same physical connections are used on 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch notebook hard disks. Pins 3,7,13 are pre-charge. Pin 11 can be used for activity indication and/or staggered spin-up. Pins 1, 2, and 3 are optional as well, as evidenced by some adapter cables that connect the drives to older PSUs. These are usually Y-adapters that have the four-pin drive connector on the other end. Currently, SATA drives rarely use 3.3 volts. That may be because there are too many people using adapters so the drive makers don't want the headaches which come with using 3.3 volts. But in the future, 3.3 volt drives may become common so you need to be careful when using SATA power cables which don't implement 3.3 volts.
Распиновка Serial ATA SATA power connector использующего разъем 15 pin SATA power.
Serial ATA is the next-generation internal storage interconnect, designed to replace parallel ATA technology Serial ATA (SATA, is a computer bus technology designed for transfer of data to and from a hard disk. It is the successor to the legacy Advanced Technology Attachment standard (ATA, also known as IDE). This older technology was retroactively renamed Parallel ATA (PATA) to distinguish it from Serial ATA. This interface uses 7-pin cables for the data connection, and transmits the data serially rather than in parallel. In addition, Serial ATA should give users the ability to hot swap hard drives. This adds a capability that more expensive systems such as SCSI and Fibre Channel have had for a long time, though the future will tell how widely users exploit that aspect of the technology. Serial ATA also reduces the signalling voltage from the 5 volts used in P-ATA down to 0.5 volts, which reduces power consumption and electrical interference. Due to serial transfer and lower power the maximum allowable length of SATA cables exceeds that of ATA ribbon cables. The Serial ATA (SATA) bus is defined over two separate connectors, one connector for the data lines and one for the power lines (SATA power pinout). A Serial ATA Hard drive may also have a third connector for legacy PATA power connections. The PATA power connector used instead of the SATA power in some early devices. Physically, the SATA power and data cables are the most noticeable change from Parallel ATA. The SATA standard defines a data cable using seven pins to supply four conductors shielded with ground supplied by the other three pins. Transmit pins are connected to Receive pins on the other side. The SATA connector is keyed at pin 7. SATA uses a 4 conductor cable with two differential pairs [Tx/Rx], plus an additional 3 grounds pins and a separate power connector. SATA runs at 150MBps(SATA/150), 300MBps(SATA II), or 600MBps transfer rates. Faster SATA implementations are backward compatible with older devices. 8B/10B encoding used for data transfers. Maximum unshielded cable length is about 1 meter. eSATA shielded cable may be up to 2 meters length. SATA interface revisions: SATA/150 (1500Mbps) - first-generation of Serial ATA interfaces, also known as SATA/150, run at 1.5 Gigahertz (GHz). Actual data transfer rate is up to 1.2 Gigabits per second (Gb/s), or 150 megabytes per second (MB/s). The simplicity of a serial link and the use of LVDS allow to use of longer drive cables. SATA 3.0Gb/s (SATA II, 3.0Gbps) - second-generation of SATA interfaces. A 3Gb/s signalling rate was added to the PHY layer. SATA II devices are required to support the original 1.5Gb/s rate. In practice, some older SATA systems require the peripheral device's speed be manually limited to 150MB/s with the use of a jumper. SATA II uses same encoding as SATA I featuring an actual data transfer rate of 2.4 Gb/s, or 300 MB/s. SATA 6.0Gb/s (SATA III, 6.0Gbps) - SATA revision 3.0 doubles the speed of the current 3Gb/s version, reaching transfer speeds of 6Gb/s. SATA drives may be plugged into Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) controllers and communicate on the same physical cable as native SAS disks. SAS disks, however, may not be plugged into a SATA controller. External SATA (eSATA) eSATA was standardized in 2004, with specifically defined cables, connectors, and signal requirements for external SATA drives. eSATA features full SATA speed for external disks, no protocol conversion from IDE/SATA to USB/Firewire, cable length up to 2m. USB and Firewire hard disks requires conversion of all communication, so external USB/Firewire enclosures include an IDE or SATA bridge chip. Some drive features (like S.M.A.R.T.) cannot be exploited that way and transfer speed with USB/Firewire bridge is limited. However, SATA does not provide power, which means that external 2.5 disks which would otherwise be powered over the USB or Firewire cable need a separate power cable when connected over eSATA.
About Serial ATA SATA SATA is the serial interface for connection of storing devices today it, basically, hard disks and it is called to replace old parallel.